Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Home
- Services
- Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common bacterial infections that affect the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. While anyone can develop a UTI, it is more prevalent in women due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. If left untreated, a UTI can progress to the kidneys, leading to more serious health complications
What is a UTI?
A UTI occurs when bacteria, primarily Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter the urinary tract and begin to multiply. The urinary tract is typically sterile, but when bacteria enter, they can cause inflammation and irritation. UTIs are classified based on the part of the urinary tract they affect:
- Cystitis (Bladder Infection): This is the most common type of UTI, causing inflammation of the bladder.
- Urethritis (Urethra Infection): Infection limited to the urethra.
- Pyelonephritis (Kidney Infection): A serious type of UTI where the infection reaches the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney damage if not treated promptly.
Causes of UTIs
UTIs occur when bacteria from the outside environment enter the urethra and travel upwards through the urinary tract. The most common cause is E. coli, a bacteria found in the gastrointestinal tract. However, other bacteria, viruses, or fungi can also cause UTIs.
Risk Factors for Developing UTIs
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men due to their shorter urethra.
- Sexual Activity: Frequent or intense sexual activity can increase the risk.
- Menopause: Hormonal changes during menopause can alter the vaginal flora, making infections more likely.
- Urinary Catheters: Using a catheter can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can create a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
- Kidney Stones or Other Blockages: Conditions that obstruct the urinary flow can lead to infections.
Symptoms of UTI
- Minimal hydration.
- Consuming supplements rich in calcium.
- Hereditary factors.
- A diet rich in animal protein
- Excessive salt intake.
- Persistent diarrhoea.
Lower Tract (Bladder and Urethra):
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- Burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Frequent, small amounts of urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Pelvic pain (common in women)
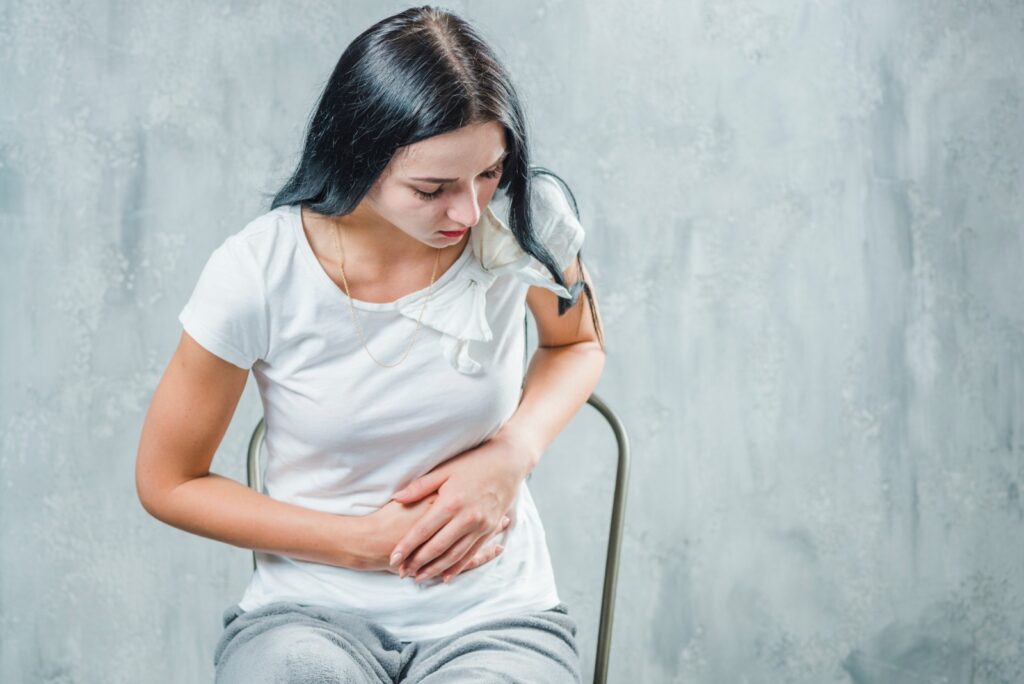

Upper Tract (Kidneys):
- Pain in the upper back or sides (flank pain)
- High fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
If you experience these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention, as a UTI can spread to the kidneys and become a serious condition.
Diagnosis of UTIs
as a UTI can spread to the kidneys and become a serious condition.To diagnose a UTI, a healthcare provider will perform a physical examination and review your symptoms. The following tests may be used for confirmation:
- Urine Analysis: A sample of your urine is tested for bacteria, white blood cells, or other signs of infection.
- Urine Culture: This test helps identify the specific bacteria causing the infection, guiding the choice of treatment.
- Imaging Tests: In recurrent UTIs or when complications are suspected, imaging tests like ultrasound or a CT scan may be recommended.
Treatment Options
UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics, which target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. The choice of antibiotic and the duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria identified.
Preventive Strategies:
- Prophylactic Antibiotics: Low-dose antibiotics may be prescribed for long-term prevention.
- Cranberry Products: Cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent UTIs in some individuals, although the evidence is mixed.
- Lifestyle Changes: Ensuring proper hygiene, staying hydrated, and urinating frequently are simple yet effective preventive measures.
UTIs in Men
Although less common, men can also develop UTIs, especially in the presence of risk factors such as an enlarged prostate, kidney stones, or a weakened immune system. When men experience a UTI, it often indicates an underlying health issue that needs to be addressed.
UTIs in Children
Children can also suffer from UTIs, and symptoms may differ from adults. Common signs include fever, irritability, bedwetting, and a lack of appetite. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications in the developing urinary system.
Preventing UTIs
While not all UTIs are preventable, there are several strategies that can reduce the risk:
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Urinating after intercourse helps remove bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity.
- Avoid irritating products like harsh soaps, douches, and deodorants in the genital area.
- Wear breathable cotton underwear to reduce moisture build-up, lowering the risk of bacterial growth.
If you experience any UTI symptoms, particularly if they are severe or recurrent, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. Untreated UTIs can lead to serious complications, including kidney damage or urosepsis (a life-threatening infection).



